Today, diseases of the external genital organs are the most common aggressive pathology. For example, long-term asymptomatic HPV infection may cause serious consequences. Certain strains of the virus can cause cancer of the rectum, vagina and cervix. Therefore, it is important to diagnose in time and start appropriate treatment.
What is HPV?
Human papillomavirus is a common infection of the reproductive tract. This pathogen has been found in almost every sixth of the inhabitants of the earth. After infection, pathogens enter epithelial cells, disrupt the division process, and activate the development of various diseases. Usually, the virus infects the organs of the genitourinary system, the anorectal area. . Diseases that occur during HPV infection:
- The formation of condyloma acuminata.
- The development of respiratory papillomatosis.
- As the tumor process progresses, damage to the genitals.
Almost 70% of the population are carriers of pathogens without clinical manifestations of the disease. It may also be infected again in a lifetime. Because not all people infected with papillomavirus are resistant to the virus.
HPV type
There are currently more than 100 types of HPV. Some of them are relatively safe for human health, while others can promote the development of tumor processes. In most cases, the clinical signs of the disease will not appear early. Usually, the first symptoms appear after the predisposing factors act.
According to tumor activity, this type of virus can be divided into:
- Strains with high carcinogenic risk (18, 16, 31, 33, etc. )
- Strains with low carcinogenic risk (6, 11, 32, 40-44, 72)
The low carcinogenicity of the virus causes skin warts and papillomas to appear on the surface of the body.
Highly carcinogenic strains cause the formation of genital warts in the genital area of the cervix of women and the penis of men.
Long-term exposure to 16, 18, 31, and 33 viruses in the body can cause abnormal cervical dysplasia and a more serious disease-cervical cancer.
However, even if HPV is present in the body with high carcinogenic risk, tumor pathology does not always occur. Calling experienced doctors in time for diagnosis and correct selection of treatment methods will enable you to never face the dangerous clinical manifestations of human papillomavirus.
How can you get infected
Both men and women are equally infected with this pathogen.
The main way of transmission is considered to be sexual behavior. Usually, HPV is infected after the first sexual intercourse, but other ways of transmission are also different:
- vertical. That is, during the passage of the birth canal of a woman infected with HPV, the newborn may be infected.
- Automatic vaccination. Self-infection (transfer from one part of the body to another) may occur during hair removal or shaving.
- Contacts and family. The human papillomavirus has survived in the environment for some time. Therefore, they may become infected after visiting public places (bathrooms, gyms, swimming pools).
- contact. It may be infected through the surface of the wound on the skin or mucous membrane (abrasions, wounds, bruises).
- Sex. The most common route of infection.
Anyone can get the virus. In order to make a timely diagnosis, you need to conduct preventive examinations with your doctor to determine the initial symptoms of the pathology.
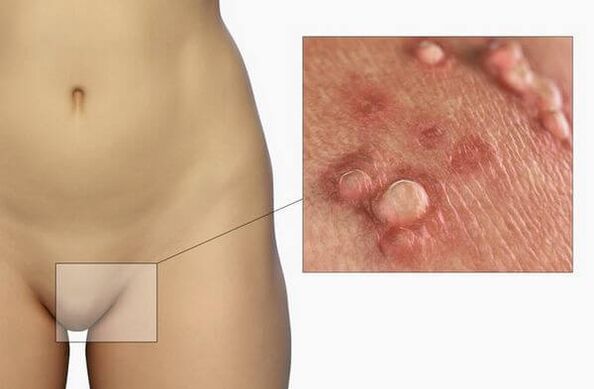
Main manifestations of infection
The presence of papillomavirus infection may not have clinical manifestations for a long time. The incubation period of the disease can last for several years, during which the patient may be infected with various types of viruses. Signs of HPV infection can only be observed after exposure to irritating factors (immune deficiency, hypothermia, stress state). In most cases, this infection will repair itself within 1-2 years, but in some patients, the pathology will become very chronic.
This disease can manifest itself in the following forms:
- Genital warts (genital warts). From the outside, these are papillary growths resembling cauliflower or comb shapes. They are flesh-colored or pink, and can be single or multiple. They can form anywhere, but are most commonly found on the skin and genital mucosa. The formation is characterized by low carcinogenicity. They rarely become malignant tumors and usually do not cause patient discomfort.
- Flat warts. They have a characteristic structure-they do not protrude above the mucosal surface of the affected organ. Such formations have high oncology potential, and therefore, they require a more thorough diagnosis. It is usually located on the vaginal wall, urethra, and cervix. In order to diagnose the nature of condyloma acuminatum, a biopsy is required.
- Atypical hyperplasia. Its characteristic is that it violates the differentiation structure of the organization. There are usually atypical cells, which can cause the development of tumor pathology.
- It requires careful observation and surgical correction if necessary.
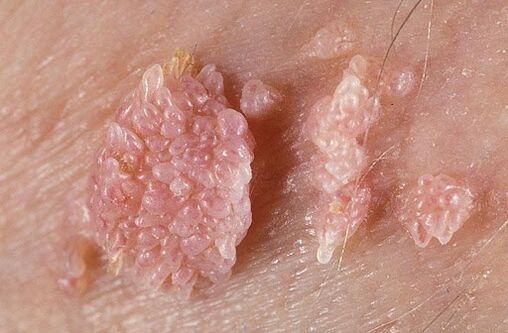
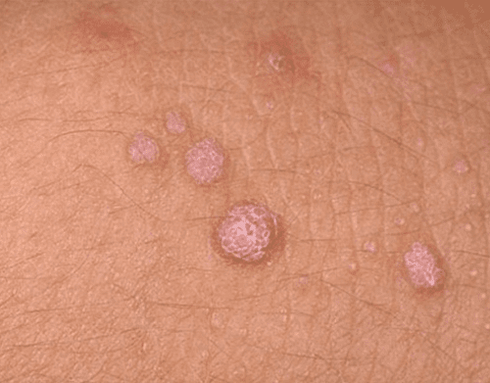
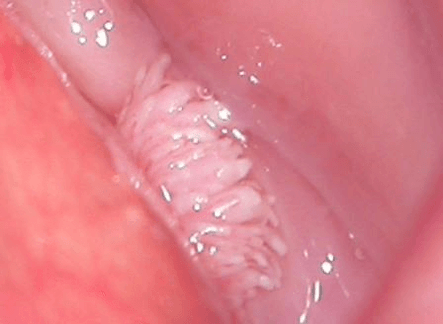
Each pathological form must be carefully monitored by a doctor. In order to reduce the risk of tumor processes, it is recommended to eliminate this growth on the skin and mucous membranes.
HPV diagnosis
It is necessary to diagnose the presence of HPV in stages; for this, many physical, laboratory and instrumental studies are used.
- Checked by a doctor. It can help identify the presence of warts. When condyloma acuminatum is found, the cervix must be examined. Ureteroscopy is also possible.
- Colposcopy. Specific tests are performed with acetic acid and iodine solutions. With their help, you can determine whether there are atypical cells, signs of HPV infection and cervical cancer.
- Cytological examination. The Pap smear is performed on the cervical mucosa. This is a screening test for the presence of precancerous cells and cancer cells in the vaginal wall or cervix wall.
Moreover, tissue histological examination can be performed to detect sexually transmitted diseases that are often associated with HPV infection. The PCR method has high diagnostic value. It can be used to identify HPV strains.
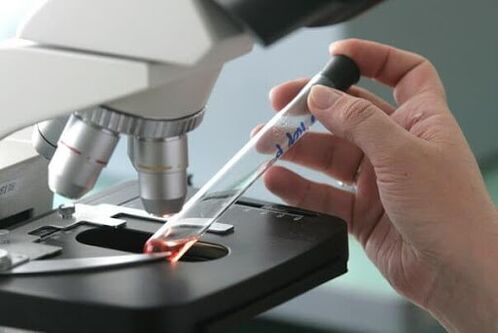
HPV (Human Papillomavirus) treatment
It is impossible to completely remove the virus from the patient's body. Doctors can only deal with the consequences of the life of the source of infection. As a general treatment, symptomatic drugs, antiviral drugs and drugs that stimulate the immune process can be used.
In order to fight various types of genital warts, the following methods can be used:
- Freezing, electrocoagulation, laser or chemical burning. This method is effective for eliminating genital warts.
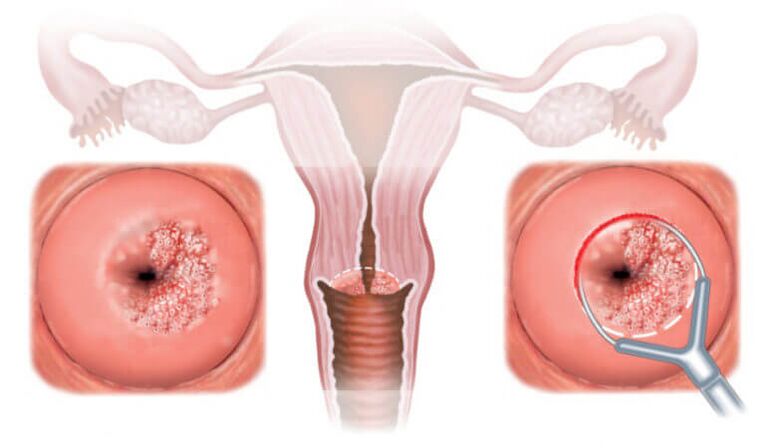
- Electrosurgical treatment is used to remove the lesions on the surface of the cervix (dysplasia, condyloma acuminatum).
Prevent HPV
In order to prevent the development of the disease, various methods are used. The most effective are:
- Monogamous relationship. You can only have sex with someone who you are the only sexual partner. This method can protect yourself from all sexually transmitted infections including HPV.
- Use barrier contraception. It is simple and affordable, but not always 100% safe from infection. Even if the damaged skin comes into contact with this area, the patient may be infected with the virus.
- Regular preventive inspections. The gynecologist needs to check the girl regularly. Therefore, you can detect the first signs of the disease and start treatment in time.
- vaccination. This is an effective and convenient method of prevention. Both men and women can be vaccinated. The most effective vaccination is before sexual activity (allowed to be used over 9 years old). Or people who have sex without contraindications.
If you suspect that there is an initial manifestation of infection or disease, be sure to consult a doctor for high-quality diagnosis and timely treatment.